The Transformative Impact of Wearable Technology in Healthcare

Introduction:
In recent years, the integration of wearable technology in healthcare has ushered in a new era of patient monitoring, preventive care, and personalized medicine. These innovative devices, ranging from smartwatches to fitness trackers, are equipped with sensors and advanced technologies that gather and analyze health-related data. This article explores the multifaceted ways in which wearable technology is revolutionizing healthcare, enhancing patient outcomes, and shaping the future of the industry.
Continuous Monitoring for Chronic Conditions:
Wearable devices enable continuous monitoring of vital signs such as heart rate, blood pressure, and glucose levels. For individuals with chronic conditions like diabetes or cardiovascular diseases, real-time data allows healthcare professionals to track trends, make informed decisions, and intervene promptly in case of abnormalities. This proactive methodology works on persistent consideration as well as diminishes medical clinic readmissions.
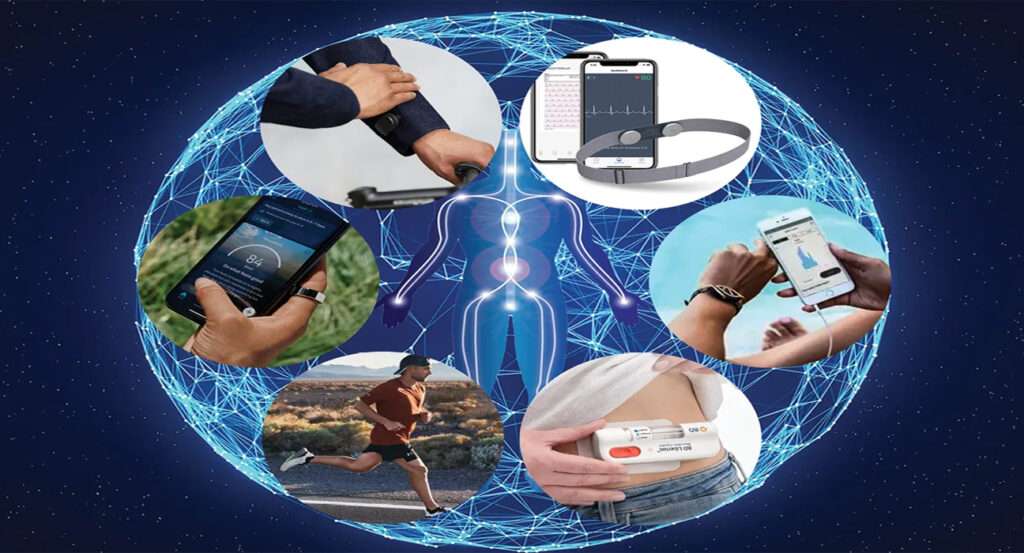
Personalized Fitness and Wellness:
Wearables have become indispensable tools for promoting preventive healthcare and encouraging a healthier lifestyle. Fitness trackers provide users with insights into their physical activity, sleep patterns, and overall wellness. By leveraging this data, individuals can set realistic health goals, monitor progress, and make informed choices to prevent lifestyle-related diseases.
Remote Patient Monitoring:
The global rise in telehealth services has been accelerated by wearable technology. Patients can now participate in remote monitoring programs, allowing healthcare providers to keep track of their health without the need for frequent clinic visits. This is particularly beneficial for those in rural or underserved areas, improving access to healthcare and reducing the burden on traditional healthcare facilities.
Early Detection of Health Issues:
Wearable devices equipped with advanced sensors can detect subtle changes in physiological parameters that may indicate the onset of health issues. For example, smartwatches with ECG capabilities can identify irregular heart rhythms, potentially leading to early detection of cardiac arrhythmias. This early warning system empowers individuals and healthcare professionals to take proactive measures, preventing the progression of diseases.
Medication Adherence and Management:
Many patients struggle with medication adherence, which can impact treatment efficacy. Wearables can be integrated with medication management systems, sending reminders and tracking medication intake. This not only helps patients stay on track with their treatment plans but also provides healthcare providers with valuable data on adherence patterns.
Data Security and Privacy Concerns:
As wearable technology becomes more prevalent in healthcare, concerns about data security and privacy emerge. This section discusses the importance of robust cybersecurity measures, compliance with data protection regulations, and the need for transparent communication to build trust among users and healthcare stakeholders.
Challenges and Future Outlook:
While wearable technology holds immense promise, challenges such as data accuracy, interoperability, and standardization need to be addressed. The article concludes by exploring ongoing research and potential future developments in wearable healthcare technology, including the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning for more accurate diagnostics and personalized treatment plans.
Conclusion:
Wearable technology is reshaping the healthcare landscape by empowering individuals, improving patient outcomes, and facilitating more efficient healthcare delivery. As these devices continue to evolve, it is crucial for healthcare professionals, policymakers, and technology developers to collaborate in addressing challenges and maximizing the potential of wearables for the benefit of global health.